

How to crack wpa2 kali install#
Playing with it requires basic knowledge of how WPA authentication works, and moderate familiarity with Kali Linux and its tools( which you can get in my previous article). Also note that, even with these tools, Wi-Fi cracking is not for beginners. There is only one way that hackers get into your network, and that is with a Linux-based OS, a wireless card capable of monitor mode, and aircrack-ng or similar.
How to crack wpa2 kali professional#
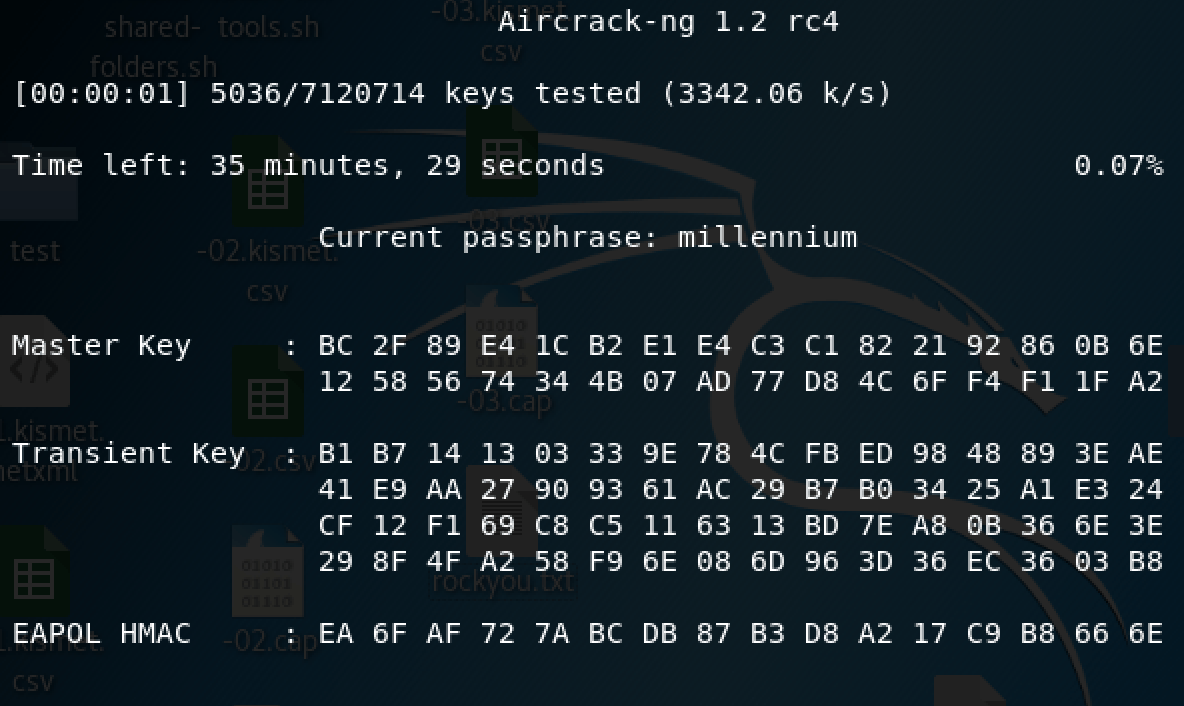
There are hundreds of Windows applications that claim they can hack WPA don’t get them! They’re just scams, used by professional hackers, to lure newbie or wannabe hackers into getting hacked themselves. $ tar -jxvf freeradius-server-2.1.12.tar.bz2Īfterwards, you will edit the configuration files in order to customize our implementation:ĭefault_eap_type = peap # Configure EAP Type to PEAPĬlient 192.168.0.Kali Linux can be used for many things, but it probably is best known for its ability to penetration test, or “hack,” WPA and WPA2 networks.
To install it in a Debian-based environment, you can run the following commands:

How to crack wpa2 kali Patch#
This patch is used to log the request made, containing credentials for authentication (challenge / response, username and password). As mentioned above, the basic components needed are a RADIUS server and an access point.Īs for the RADIUS server, we will use FreeRADIUS v2.1.12, one of the most popular open source RADIUS server, with the Wireless Pwnage Edition patch. This step of preparation is used to simulate the real network and make believe clients to connect to actual infrastructure. The first thing to do before starting the attack is to create the infrastructure to replicate the enterprise environment of wireless network, which should be as equal as possible to the target. However, this information, EAP type especially, can be identified by inspecting the EAP handshake using a sniffer (e.g. To make this type of attack you need to be physically proximity to the target, especially staying within the action range of enterprise access point.ĭuring a typical attack, there is also the phase of reconnaissance in order to identify all access points, clients and gather the most information as possible about the target, in particular technologies and implementations. The attack consists of spoofing the target network and provide a better signal to the client than legitimate access point, in order to perform a Man-In-The-Middle attack between clients and network infrastructure, because currently the TLS tunnel is enough secure and not easily attackable. The methodological approach used is composed of a first step of preparation of the network infrastructure, followed by an enumeration of wireless devices and finally the attack phase to the connected clients in order to get the credentials. Although if technically different, they operate similar providing security through a TLS tunnel to ensure credentials cannot be sniffed, unlike other EAP configurations. This article will focus on deploying EAP-TTLS (with Tunneled Transport Layer Security) and PEAP (Protected EAP) those implementations are the most widespread in the Wi-Fi enterprise nowadays, because they are considered very resilient to attacks. This technology relies on the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to send messages between the supplicant and the authentication server, allowing multiple implementations for corporations to encapsulate the packets: EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS/MSCHAPv2, PEAP/EAP-MSCHAPv2, PEAP/EAP-GTC, PEAP-TLS, EAP-SIM, EAP-AKA, EAP-FAST and LEAP. The authenticator is typically an enterprise access point, which interfaces with the authentication server, implemented through RADIUS or IAS protocol, to validate and authenticate the user client. The supplicant is a client device that is responsible for making requests to the WLAN, providing credentials to the authenticator. WPA-Enterprise standard, also known as WPA-802.1X, is designed for enterprise wireless networks using a supplicant, an authenticator and an authentication server. Wireless communication can contain a lot of sensitive information that, if an unauthorized user is able to sniff or connect to the wireless access point, could retrieve and consequently compromise the confidentiality, integrity and availability of organizations data. This allows flexibility and centralized governance for domain accounts. WPA-Enterprise is ideal for corporations: it does not use a single PSK in which all users use to connect to the wireless network, but each user has their own credentials that they use to authenticate to the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
